Blog Archives
Cries and Whispers, 1972, Ingmar Bergman

By 1972, Bergman was already established as one of the titans of international art cinema. He had won several awards at Cannes and been nominated for two Academy Awards (he would eventually be nominated for 9, including three for this film). Cries and Whispers is not a film that could be made by anyone. It could not have been made by Ingmar in his younger years. It could be seen as a spiritual sequel to Persona, which was really his first foray intro surrealism and immersive, abstract character exploration. Cries and Whispers does not share many thematic or plot elements with this predecessor, but it does utilize the supernatural and it explores these four characters nearly as deeply as the two (or one?) in Persona.
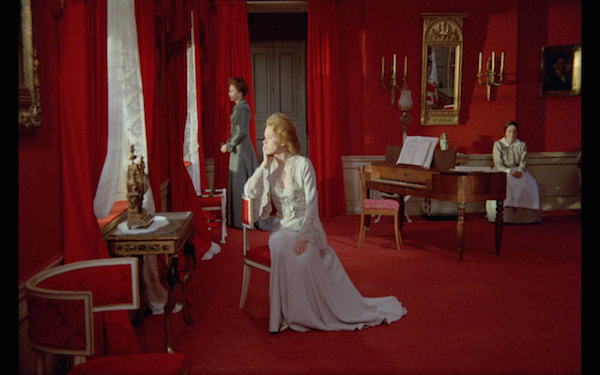
Another similarity between this and Persona is the visual canvas. Persona was in black and white, but I think of it as starkly black and starkly white, almost to the point where it has the same effect as a color film. Cries and Whispers is a color film, but it is nearly a red and white film. The reds are stark and stunning, while the whites are a contrast, just like the whites were in Persona. The colors are visual motifs as well, as red signifies death, mutilation, and white represents the innocence of a lost and nearly forgotten childhood. Sven Nykvist rightfully won an Oscar for his work, and Bergman and crew deserve praise for creating such a visually remarkable red-and-white world.

The color of red is used most effectively for the scene transitions. At the end of a scene, the image dissolves into a red canvas, which gives it a surreal quality. It is a continual reminder of the central theme of death, as Agnes fights her battle with uterine cancer. Sometimes Bergman freezes in the middle of the dissolve, holding on the blood red screen to give us time to ponder and process the meaning of the scene. These transitions and the slight deviations with each one heightens the impact of the color red. I can think of many movies that have used a single color to dictate the theme, some of which are done well (Kieslowski’s Red for example), but none that used it to this extreme, creating what is basically a red and white film.
Please be warned that from here on our I will be delving into spoiler territory.
Harriet Andersson as Agnes gives the most memorable and challenging performance as she tries to cope with the pain and her imminent, unavoidable death. The anguish on her face is heartbreaking and convincing. Much of her performance is given in grunts and grimaces. She is at her most vocal at the very end of the film, but this is after she has passed and the pain has left her. Only the loneliness and the yearning for comfort remains. She seeks solace from her two sisters, yet receives it only from her housemaid Anna (Kari Sylwan) in an unusual yet effective manner.
The sisters, Maria (Liv Ullmann) and Karin (Ingrid Thulin) are complicated characters, at times polar opposite from each other, yet there is some grey (or red?) area in between. To her sisters, Karin is stoic and stubborn, refusing and being repulsed by intimate contact. Maria is affectionate and compassionate, yet she is unscrupulous, making out with the doctor watching over Agnes. In flashback we see Maria and the doctor having an affair, which results in her husband attempting suicide. Karin also flashes back, but her memory is of fidelity and mutilation. She says “nothing but a web of lies” as she abuses herself with broken glass and then exhibits a grisly scene for her stunned husband.
At Agnes’ funeral, the priest says that they had many talks and her faith was stronger than his. Is this why she is able to come back? This is never explained, but the ensuing revisitation with Anna and the sisters has differing results. Maria, who was affectionate to Agnes in life, rejects her in death. Karin also rejects and hates her resurrected sister. Again, the only character that gives her any comfort is Anna, yet the living relatives treat her with scorn and dismiss her as if she was a piece of trash.
The film can be interpreted a number of ways. It speaks to the intimacy (or lack thereof) of family, and how familial love and companionship is fleeting and unobtainable in later life and especially in death. It speaks to the wickedness of the upper class, and how true camaraderie and goodness comes from those that are not clouded by a privileged upbringing. It also says that personal relationships are ultimately rooted in selfishness. With their husbands and other sisters, the sisters care only for what they receive. The same is true about Agnes, who we learn little about, but she is also selfish for intimacy and companionship. The only true altruistic and benevolent character is Anna. She pledges to care for Agnes in life and in death with no financial recompense. At least Maria, who despite her flaws is the most considerate of the other primary characters, and gives Anna a little something to help. Maybe there is hope for humanity yet.
Film Rating: 8/10
Supplements
Bergman Introduction: 2003 on the Island of Fårö.
This project came about in winter on the island. It was melanchology time for him because he had just been broken up with someone. He was lonely with only a Dachshund to keep him company. He had an image of a room completely in red. He believes that if the image persists, you should keep writing.
Harriet Andersson – 2012 Stockholm interview with Peter Cowie.
This was just like the interview on the Summer with Monika disc, and was probably recorded in the same session. Harriet was again very animated and descriptive. She is a great interview at an older age.
It had been 10 years since she had worked with Ingmar. At first she rejected the part because it was too difficult. He said, “Don’t give me that load of crap,” and she took it.
The castle set was wonderful. They had offices downstairs. The red rooms were the studio on the main floor. The floor above was for make-up and wardrobe. Ingmar had said the red room resembled the inside of the womb. Andresson: “Well he says things.” “He like to make small stories.” She implies that he is telling a tale.
They kept her awake at night and that made her look tired. The death scenes were an imitation of her father, which she witnessed. He had a terrible death. She has trouble watching the film now because of that memory.
On-set Footage Silent color footage with audio commentary from Peter Cowie.
This is the highlight of the disc. They have quite a bit of silent behind the scenes footage that includes the set-up, press conference, actresses on location in and out of the house, the cast and crew being fed, editing of the film, rehearsals, and so forth. It is a wealth of material and Cowie gives numerous factoids on the film just by talking over the images. This was almost as satisfying as a good audio commentary.
They talk a great deal about the playwright Strindberg. He had spent summers at the manor that they used as a boy and took inspiration of Miss Julie from lady of the manor. Bergman had adapted Strindberg plays for stage, but never for film. One interesting point is that Bergman’s films were not very popular in his home country, but his Strinberg plays were exceptionally popular.
Ingmar Bergman Reflections on Life, Death and Love: 1999 television interview with Erland Josephson.
This is another enjoyable interview. They do not talk about the films so much as they do personal lives, loves, relationships, and various other topics. Bergman is surprisingly candid.
They talk about children. They both have quite a few (Bergman has nine). Bergman talks about apologizing to one of his children for being a terrible father, when the son says that he hasn’t been a father at all. They all get together every year at Fårö Island and the children have maintained good relationships. None of his children were planned. “They were all love children.”
The women lasted about 5 years until he found a new one, and then he found Ingrid, and then she died. When she decided to marry him, “all other traffic ceased.” He was truly in love. He is friendly with all the other girls that he was ever with, and many (including Liv and Harriet) became part of his acting stable. Elrand points out that all the bitterness subsides over time. With Ingrid he had a close relationship, and he has reverted to solitude now that she’s gone.
They talk about death and the inevitability, and how Ingmar doesn’t fear it so much but Elrand does. Of course he talks about Ingrid and how he planned to leave Fårö to her, but her passing happened and it crushed him. You can tell that his life was still devastated by it even all those years later.
On Solace: Video Essay from :kogodana:.
This is an interesting essay, unlike most on Criterion discs. It uses images and text well, especially the red title cards with white text.
The concept of the three movements is abstract to a degree, and it is easier to watch than for me to explain it here. Basically he says that there are three movements. The first two movements are flashbacks, while the third is a distillation.
He points out a few insightful observations, such as that Karin’s mutilation is inverse of Agnes’ uterine cancer. The final scene recalls “bodily solace” that Anna gives Agnes in earlier scene, which is the central theme of the movie and the thesis of his essay.
Criterion Rating: 9/10
Summer With Monika, 1953, Ingmar Bergman

For this post I am mixing it up a little bit. Rather than do a formal review, I’m participating in MovieMovieBlogBlog’s Sex! Blogathon. Rather than do a formal review and/or analysis of this earlier Bergman film, I’m going to explore how sexuality was portrayed and how revolutionary it was in the world of cinema.
Monika and Harry are like many young, lusty couples. We see the courting process with them watching a romantic movie together. She is in tears while he yawns, which is typical, but through their brief time together they establish a deep, romantic connection. From there they escalate to a sexual relationship.
Even though Bergman had not launched on the internal stage just yet as a major auteur, by 1952-53, he had honed his filmmaking craft. The film language he used in films like Summer with Monika and previously in Summer Interlude would remain relatively constant throughout the rest of his career, but of course he improved and became more capable over time. He also showed early on a keen ability to demonstrate romanticism, sensuality and even sexuality. Because of the Hay’s code, American filmmakers had learned the power of suggestion through film language to hide the overt sexuality in film. Bergman borrowed some of these hints and developed a few methods of his own, but he also not afraid to dip his toes in the water and explore sexuality more directly.
We know that Monika and Harry begin an attempt at escalating the physical relationship because they are in the midst of some heavy petting when her father comes home. They quickly dress and act as if nothing was happening, which is a subterfuge that many (probably even Bergman) can identify with. They then meet on the boat and presumably have sex. They are in the same bed and there are vague suggestions at sexual activity. Harry loses his job and does not care. His new job is within the arms of Monika. As he ventures away from the city with her, we see the city from the boat’s point of view. The camera rocks back and forth, which we would expect from a floating boat, but in my opinion it is rocking because of the activities taking place within. Later in the film we learn that Monika has become pregnant. Conception most likely took place during these early scenes.
The sexuality transforms from suggestion to depiction as they reach the island. We first see Monika wearing a revealing bottom and a loose shirt, which she takes off. This is only the beginning of a series of scenes with a scantily clad Harriet Andersson. As they settle on the island, we see what is quite close to nudity. She faces Harry and removes her top, revealing her nude back. We then see her from Harry’s perspective, but his body blocks any nudity from showing on camera, yet his wandering hands clearly reach those same hidden areas. Monika gets up and runs to the beach and we see her naked behind, and then the film cuts to her in a natural pool. This scene is tame by today’s standards, but for 1953, it was quite scandalous.
The relationship and plot play out over the summer, and since this is not a traditional review, I’m going to skip these details. As they get settled back in the city, Monika becomes weary with her relationship and strays elsewhere. Bergman communicates this by simply having her look at the camera seductively when we know she is out of the house and away from Harry. This was also scandalous, because this was a sexually licentious woman. People in film were not often portrayed as straying from a committed relationship or marriage, even if it was only hinted at (although confirmed later) like in Bergman’s film.
In one of the final scenes, Bergman goes for the gusto. We see Harry raising his little girl, betrayed and rejected by Monika, but that summer still enraptures him. It isn’t clear whether the sexual escapades or the romantic moments are the most magical in his memories, but the version of Monika in the summer was a fairy tale. We see a flashback from his perspective of Monika in the same near-nude sequence as earlier, but this time the film does not cut as she runs to the beach with her rear exposed. She is fully nude, although this is a long shot so, again, not very explicit to modern eyes, but progressive for back then. Given that Harry remembers that one, erotic image, I think it was his personal sexual revolution that he longs for.
Film Rating: 8/10
Supplements
Ingmar Bergman Intro:
This is a brief introduction from 2003. Bergman felt affection for the film because of the way the screenplay came together, but also because of his introduction to Harriet Andersson. He had seen her in a stage play in fishnet stockings and lace, so he wanted her to be in the part. He did not go into the fact that they became lovers.
Harriet Andersson: 2012 Interview with Peter Cowie.
It had been 60 years and for her age, she looked remarkable. She speaks English well, with a strong accent. She talks about her origins in the industry, from being picked out to working with Bergman.
Bergman’s reputation in Sweden was very poor among actors at the time. He was reputed to yell and scream at them, and had his eye on young girls (which isn’t entirely inaccurate). She auditioned with an 8-minute shot where she was sketchy with her lines. She was surprised to get the part, which was a dream part.
She was not worried about the nudity. They were on an island so it felt natural, and the crew had seen it already. It felt liberating.
They talk about her looking at the camera, which was a scene that was appreciated by the French New Wave. She was shocked at the scene at first because this was something that wasn’t seen. People didn’t look at the camera. She thought it was strange, but went along with it.
Because of being lucky in getting this famous role, she was able to get roles with other directors and of course many future Bergman films. It was a break-out role for her.
Images from the Playground: .
This half-hour documentary is introduced by Martin Scorsese, who produced it through World Cinema Foundation. He was fortunate enough to live through Bergman’s career genesis from Summer with Monika up to Saraband. The documentary has behind the scenes footage from Bergman working on the film. It is from Bergman’s 9.5mm camera, and is almost like a home, silent video. It has narration from audio interviews of Bergman and his stable of actresses.
They talk about the production, such as Bergman discovering Harriet and talking about how gorgeous she was. It is interesting to see this commentary, but it is easier to just get caught up in the images and narrative. They take the documentary beyond just Summer with Monika. Bibi and Liv also participate. Bergman talks about the importance of all of these actresses and there are reflections on the fact that Ingmar was involved with them intimately at some stage.
This really is a magnificent little piece of film. It is the treasure of the disc.
Monika, Exploited!
Summer with Monika was a controversial picture in the states, and was hacked up and released as exploitation-fare with an English dub. This is an interview with Eric Schaefer who talks about how it became exploitation fodder.
During post-war period, distributors were importing films from overseas with adult content. These arthouse films were released in the exploitation circuit. Monika fit well with this market because of the brief nudity and sensuality.
Kroger Babb, an exploitation exhibitor, got the rights to Summers with Monika for $10,000. He then put in $50,000 into the film for cutting and dubbing. He got it through deceptive and suspect means, and Svensk took legal action because they soid the rights to Janus Films. They worked out a deal to release “Stories of a Bad Girl,” Babb’s version for five years, while Janus would release it for art audiences.
Criterion Rating: 8.5/10